Auteur : Lay Wen.
Les normes de prise de la National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) jouent un rôle crucial dans l'écosystème de recharge des véhicules électriques (VE). Choisir le bon type de prise NEMA garantit la compatibilité, la sécurité et l'efficacité de la charge pour les chargeurs domestiques et portables. Ce guide explore les types de prises NEMA les plus courants pour la recharge des VE (NEMA 5-15 , 6-20 et 14-50) , en expliquant leurs principales différences, leurs applications et comment choisir la prise la plus adaptée à vos besoins.
1. Que sont les prises NEMA ?
Les prises NEMA sont des connecteurs électriques normalisés définis par la National Electrical Manufacturers Association. Chaque code de prise NEMA (par exemple, NEMA 14-50P) indique une configuration spécifique de tension, d'ampérage, de mise à la terre et de forme de broche. Pour la recharge de véhicules électriques, le type de prise détermine la puissance que votre chargeur peut prélever en toute sécurité sur une prise domestique ou commerciale.
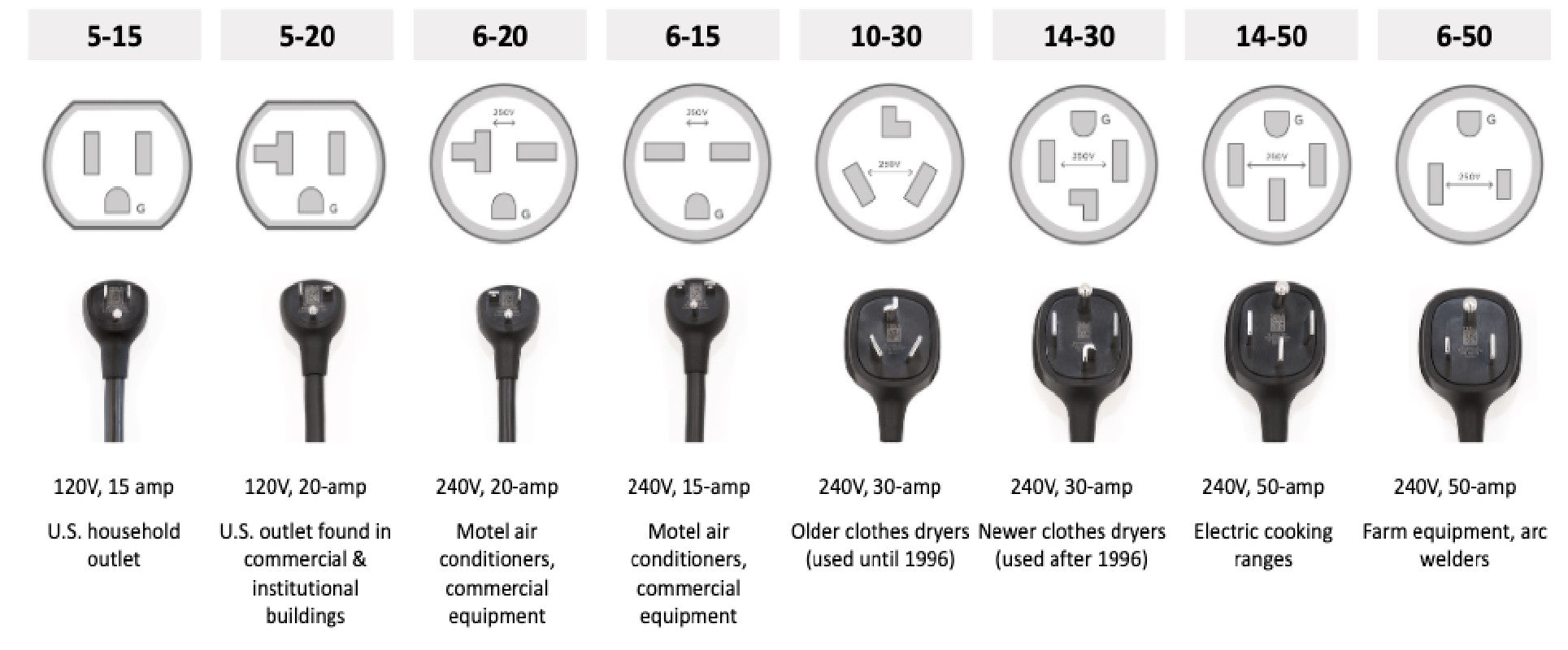
2. Types de prises NEMA courantes pour la recharge des véhicules électriques
NEMA 5-15 (charge de niveau 1)
-
Tension/Ampérage : 120 V, 15 A
-
Utilisation typique : prises domestiques standard
-
Vitesse de charge : environ 3 à 5 miles d'autonomie par heure
-
Avantages : Universellement disponible
-
Inconvénients : Vitesse de chargement très lente
NEMA 6-20 (charge de niveau 2)
-
Tension/Ampérage : 240 V, 20 A
-
Utilisation typique : Appareils légers, ateliers
-
Vitesse de charge : environ 10 à 15 miles d'autonomie par heure
-
Avantages : Plus rapide que NEMA 5-15, moindre coût d'infrastructure
-
Inconvénients : Moins courant dans les maisons
NEMA 14-50 (charge de niveau 2)
-
Tension/Ampérage : 240 V, 50 A
-
Utilisation typique : parcs de camping-cars, séchoirs, prises de courant dédiées aux véhicules électriques
-
Vitesse de charge : environ 25 à 37 miles d'autonomie par heure
-
Avantages : Charge rapide, largement prise en charge par les chargeurs de véhicules électriques
-
Inconvénients : Peut nécessiter l'installation d'un électricien
3. Choisir la bonne prise NEMA pour votre véhicule électrique
| Type de prise | Tension | Amplis | Utilisation typique | Vitesse de charge | Idéal pour |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 5-15 | 120 V | 15A | Prise standard | 3 à 5 mi/h | Recharge nocturne à domicile |
| NEMA 6-20 | 240 V | 20A | Atelier Garage | 10-15 mi/h | Utilisateurs à domicile soucieux de leur budget |
| NEMA 14-50 | 240 V | 50A | Prise pour camping-car/cuisinière électrique | 25-37 mi/h | Conducteurs fréquents, recharge à domicile la plus rapide |
Lors de la sélection d'un type de prise, tenez compte de la capacité de la batterie de votre véhicule électrique, du kilométrage quotidien moyen et de la capacité du panneau électrique.
4. Considérations relatives à l'installation et à la sécurité
-
Permis : L'installation de prises 240 V (6-20 ou 14-50) nécessite généralement un électricien agréé.
-
Charge du circuit : assurez-vous que votre disjoncteur peut gérer l'ampérage.
-
Étanchéité : En cas d’installation à l’extérieur, utiliser des boîtiers résistants aux intempéries.
5. Pérennisation grâce à des adaptateurs interchangeables
De nombreux chargeurs pour véhicules électriques sont fournis avec des kits d'adaptation ou des embouts interchangeables permettant une utilisation avec plusieurs prises NEMA. Choisir un chargeur avec des options de prises flexibles peut faciliter les déplacements et les mises à niveau futures.
Lecture recommandée : NEMA 5-15 vs 6-20 vs 14-50 : choisir la prise adaptée à la charge des véhicules électriques







Partager:
Guide d'achat de bornes de recharge pour véhicules électriques : comment choisir la solution de recharge à domicile adaptée
Comprendre les adaptateurs pour véhicules électriques : améliorer la compatibilité entre les normes de recharge