Author: Lay Wen.
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) plug standards play a crucial role in the electric vehicle (EV) charging ecosystem. Choosing the right NEMA plug type ensures compatibility, safety, and efficient charging performance for home and portable EV chargers. This guide explores the most common NEMA plug types used in EV charging—NEMA 5-15, 6-20, and 14-50—explaining their key differences, applications, and how to select the right one based on your charging needs.
1. What Are NEMA Plugs?
NEMA plugs are standardized electrical connectors defined by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association. Each NEMA plug code (e.g., NEMA 14-50P) denotes a specific configuration of voltage, amperage, grounding, and prong shape. For EV charging, the plug type determines how much power your charger can safely draw from a home or commercial outlet.
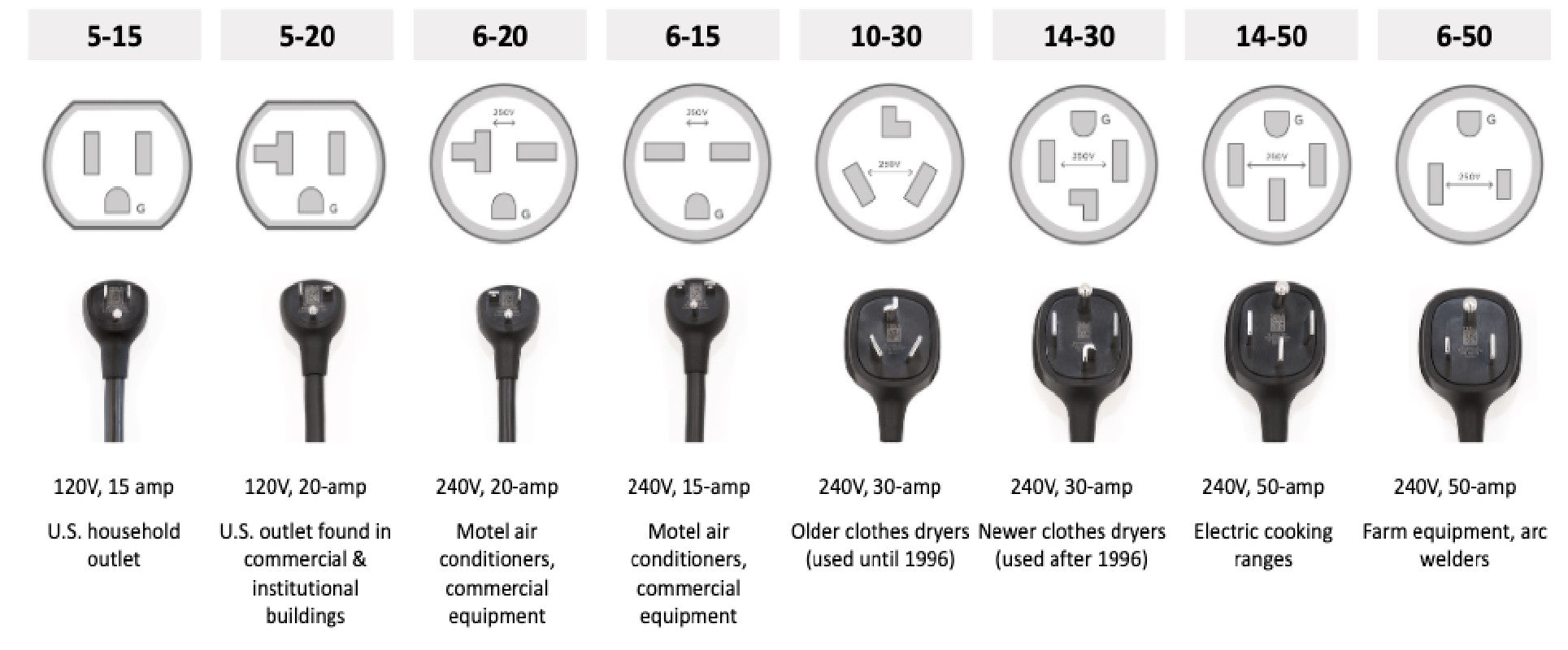
2. Common NEMA Plug Types for EV Charging
NEMA 5-15 (Level 1 Charging)
-
Voltage/Amperage: 120V, 15A
-
Typical Use: Standard household outlets
-
Charging Speed: ~3-5 miles of range per hour
-
Pros: Universally available
-
Cons: Very slow charging speed
NEMA 6-20 (Level 2 Charging)
-
Voltage/Amperage: 240V, 20A
-
Typical Use: Light-duty appliances, workshops
-
Charging Speed: ~10-15 miles of range per hour
-
Pros: Faster than NEMA 5-15, less infrastructure cost
-
Cons: Not as common in homes
NEMA 14-50 (Level 2 Charging)
-
Voltage/Amperage: 240V, 50A
-
Typical Use: RV parks, dryers, dedicated EV outlets
-
Charging Speed: ~25-37 miles of range per hour
-
Pros: Fast charging, widely supported by EV chargers
-
Cons: May require electrician installation
3. Choosing the Right NEMA Plug for Your EV
| Plug Type | Voltage | Amps | Typical Use | Charging Speed | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 5-15 | 120V | 15A | Standard Outlet | 3-5 mi/hr | Overnight charging at home |
| NEMA 6-20 | 240V | 20A | Workshop Garage | 10-15 mi/hr | Budget-conscious home users |
| NEMA 14-50 | 240V | 50A | RV/Electric Stove Outlet | 25-37 mi/hr | Frequent drivers, fastest home charging |
When selecting a plug type, consider your EV’s battery capacity, average daily mileage, and electrical panel capacity.
4. Installation and Safety Considerations
-
Permits: Installation of 240V outlets (6-20 or 14-50) usually requires a licensed electrician.
-
Circuit Load: Ensure your circuit breaker can handle the amperage.
-
Weatherproofing: If installed outdoors, use weather-resistant enclosures.
5. Future-Proofing with Interchangeable Adapters
Many EV chargers come with adapter kits or interchangeable plug ends to allow use with multiple NEMA outlets. Choosing a charger with flexible plug options can help accommodate travel and future upgrades.
Recommend Reading: NEMA 5-15 vs 6-20 vs 14-50: Choosing the Right Plug for EV Charging Needs







Share:
EV Charger Buying Guide: How to Choose the Right Home Charging Solution
Understanding EV Adapters: Bridging Compatibility Across Charging Standards