As electric vehicles (EVs) become mainstream, understanding the core components that make them function is essential for drivers, fleet operators, and charging equipment manufacturers alike. One of the most crucial components is the Onboard Charger (OBC)—the invisible bridge between AC wall outlets and your EV's high-voltage battery pack.
This article explains what an OBC is, how it works, its power ratings, and why it matters for charging efficiency and safety.
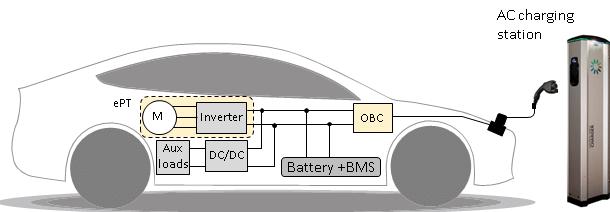
What Is an Onboard Charger (OBC)?
An Onboard Charger (OBC) is a built-in power conversion system located within an electric vehicle. Its main job is to convert alternating current (AC)—typically from a home outlet or AC public charger—into direct current (DC) that can safely charge the vehicle's high-voltage battery pack.
Key Functions:
-
AC to DC Conversion
The OBC acts like a rectifier, converting grid power (AC) into the DC format batteries require. -
Voltage Regulation
Ensures that the current entering the battery is properly regulated to prevent overcharging or overheating. -
Communication with EVSE
The OBC “talks” to the charging station to negotiate current levels, initiate charging, and manage safety protocols.
How Does an OBC Work?
When you plug your EV into an AC Level 1 (120V) or AC Level 2 (240V) charger, power flows through the charging cable to the vehicle’s inlet. The OBC receives this AC current and performs the following steps:
-
Rectification: Converts AC into DC via internal power electronics.
-
Voltage Transformation: Adjusts voltage levels using internal transformers or regulators.
-
Battery Management Integration: Coordinates with the Battery Management System (BMS) to deliver the right current based on temperature, battery health, and state-of-charge.
-
Safety Monitoring: Controls shutoff and relays if a fault is detected during the charging session.
OBC Power Ratings and Charging Speed
The power rating of an OBC determines how quickly your EV can charge on an AC charger. It is usually measured in kilowatts (kW). Here are common OBC capacities:
| OBC Rating | Max AC Input Voltage | Max Charging Power | Approx. Charging Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3 kW | 240V | 3.3 kWh/hr | ~10–12 miles/hr |
| 6.6 kW | 240V | 6.6 kWh/hr | ~20–25 miles/hr |
| 11 kW | 240V / 3-phase | 11 kWh/hr | ~35–40 miles/hr |
| 22 kW | 400V / 3-phase | 22 kWh/hr | ~65–70 miles/hr |
⚠️ Note: Even if the EVSE provides 22 kW, your car can only charge at the OBC’s max rating.
OBC vs. DC Fast Charging: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Onboard Charger (OBC) | DC Fast Charging (No OBC used) |
|---|---|---|
| Current Type | AC | DC |
| Charging Speed | Slower | Much Faster |
| Location of Charger | Inside the EV | External (in charger cabinet) |
| Power Rating | Typically 3.3–22 kW | 50–350+ kW |
| Use Case | Home / Workplace / AC Public | Long trips / Highway corridors |
In DC fast charging, the vehicle bypasses the OBC entirely, as the external charger delivers DC directly to the battery. This allows for much higher power delivery, such as 150 kW or more.
Why OBC Quality Matters
Not all OBCs are created equal. A high-quality OBC ensures:
-
Stable charging performance
-
Battery longevity by preventing thermal or voltage stress
-
Compatibility with global AC standards
-
Efficient power conversion, minimizing heat loss
That’s why many EV brands—and accessory makers like EVDANCE—optimize their products around OBC specifications to guarantee reliable charging.
Future Trends: Bi-Directional OBCs and V2G
Advanced Onboard Chargers are now being developed with bi-directional capability, enabling Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) and Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) features.
These allow your EV not just to consume electricity but also to supply it when needed, acting like a mobile battery for your home or local grid during outages or peak hours.
Infographic: How an Onboard Charger Works in an EV

Final Thoughts: OBCs Are the Heart of AC Charging
While EVs are praised for their sleek exteriors and instant torque, it’s the unseen components like the Onboard Charger (OBC) that ensure every home charge is safe, efficient, and battery-friendly. Understanding how the OBC works empowers owners to make better decisions about charging equipment, extension cords, and even route planning.
As EVDANCE continues to offer premium charging solutions—from extension cords to adapters—it’s essential to choose tools compatible with your vehicle’s OBC specs.
Written by: Lay Wen
Recommended reading: Understanding the ICCU in Electric Vehicles: What It Is and Why It Matters







Share:
Why My Tesla NACS Adapter Isn't Working: Understanding the Core Issues
What Is a Vehicle Charging Control Unit (VCCU)?