Author: Lay Wen
In the world of electrical connectors, particularly for electric dryers and EV chargers, two plug types frequently come up: NEMA 10-30P and NEMA 14-30P. While they may appear similar and serve comparable purposes, their technical differences and usage contexts are critical for both safety and compatibility.
This article explores the distinctions between NEMA 10-30P and 14-30P plugs, their current applications, and considerations for EV owners and homeowners making infrastructure decisions.
Key Differences Between NEMA 10-30P and NEMA 14-30P

The Aging 10-30P Standard
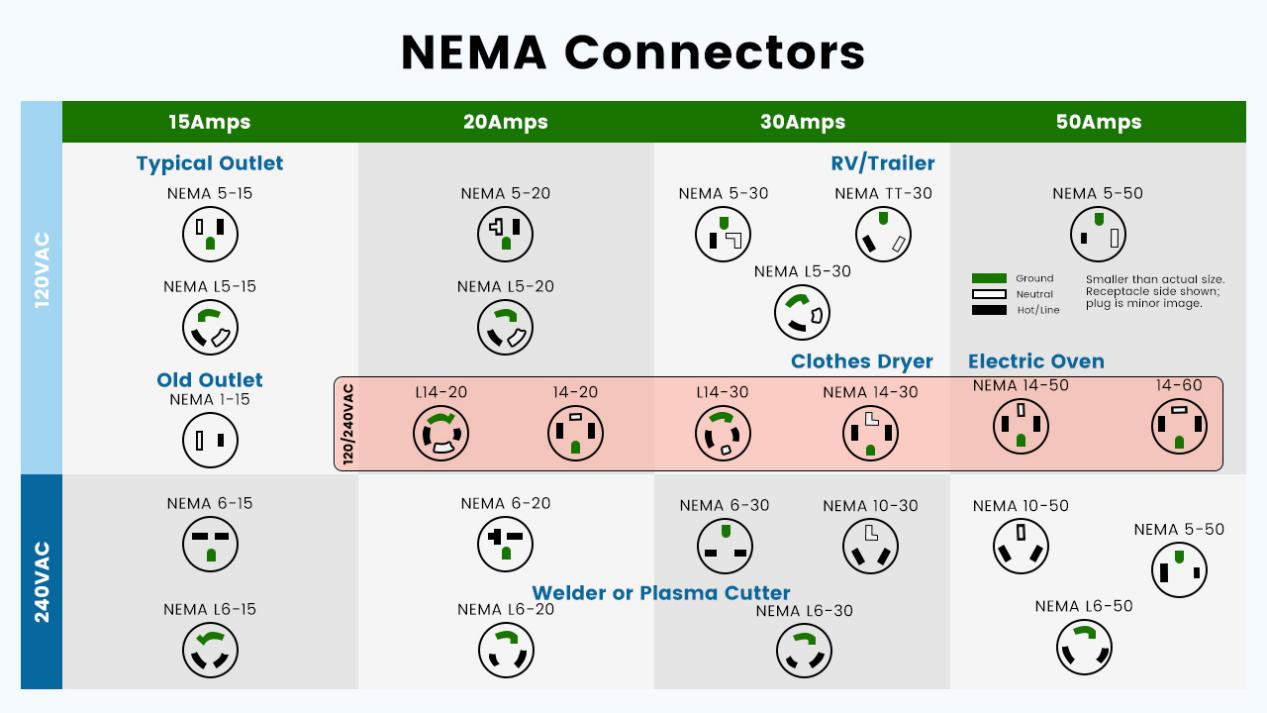
NEMA 10-30P plugs were common in homes built before the mid-1990s. These plugs lack a dedicated ground wire, relying on the neutral for grounding—a practice now considered unsafe by modern standards. As a result, the National Electrical Code (NEC) no longer recommends installing 10-30P outlets in new construction or renovations.
Despite this, many older homes still feature 10-30P outlets, especially for dryers. EV owners in such homes often use adapters to connect modern Level 2 chargers. However, caution is advised due to the lack of grounding, which can pose a fire or shock hazard.
The Modern 14-30P Advantage
NEMA 14-30P plugs, in contrast, include a separate ground wire, making them compliant with NEC standards and significantly safer for high-power applications such as electric dryers and EV charging.
Many modern EV charging systems—including Tesla’s Mobile Connector—support 14-30P plugs directly or via approved adapters. Homeowners installing new EV outlets or upgrading old ones should strongly consider transitioning to 14-30P for both compliance and peace of mind.
Which One Should You Use?
If you already have a NEMA 10-30P outlet:
-
Use it with caution and only with properly rated adapters that mitigate safety risks.
-
Consider upgrading to a 14-30P outlet during your next electrical upgrade.
If you’re installing a new outlet for an EV charger:
-
Go with a NEMA 14-30P. It’s safer, code-compliant, and widely compatible with EV equipment.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between NEMA 10-30P and 14-30P plugs is essential, especially in the growing age of home electrification and EV adoption. While 10-30P still lingers in legacy systems, the 14-30P is the clear choice for future-proofing your home and ensuring safe, reliable charging for your electric vehicle.
Recommend Reading: Understanding the NEMA 14-30 Plug for EV Charging: A Complete Guide







Share:
EV Depreciation Explained: Models That Keep Their Value
Why the NEMA 14-30 Plug Is a Smart Choice for Home EV Charging