As electric vehicles (EVs) grow in popularity, so do the possibilities they bring beyond mobility. One of the most transformative concepts gaining traction is V2G, or Vehicle-to-Grid technology. V2G enables bidirectional energy flow between an electric vehicle and the power grid, turning EVs from energy consumers into flexible energy assets.
This article explores how V2G works, its applications, benefits, and challenges—and why it's poised to play a key role in building a resilient, renewable-powered grid.
What Is V2G Technology?
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) refers to a system where electric vehicles can discharge stored electricity back to the power grid or to a building when needed. Using bidirectional chargers, EV batteries become temporary energy storage units that support grid stability.
In contrast to traditional EV charging—which only draws energy from the grid—V2G systems allow electricity to flow in both directions.
How V2G Works
-
Energy Storage
EVs charge their batteries during off-peak periods when electricity is cheaper or when renewable energy supply is high (e.g., solar in the afternoon). -
Energy Discharge
During peak demand or outages, EVs connected to V2G-capable chargers can send power back to the grid or supply power to homes and buildings. -
Grid Communication
Smart chargers communicate with utility companies to manage energy dispatching based on grid demand, pricing, and capacity.
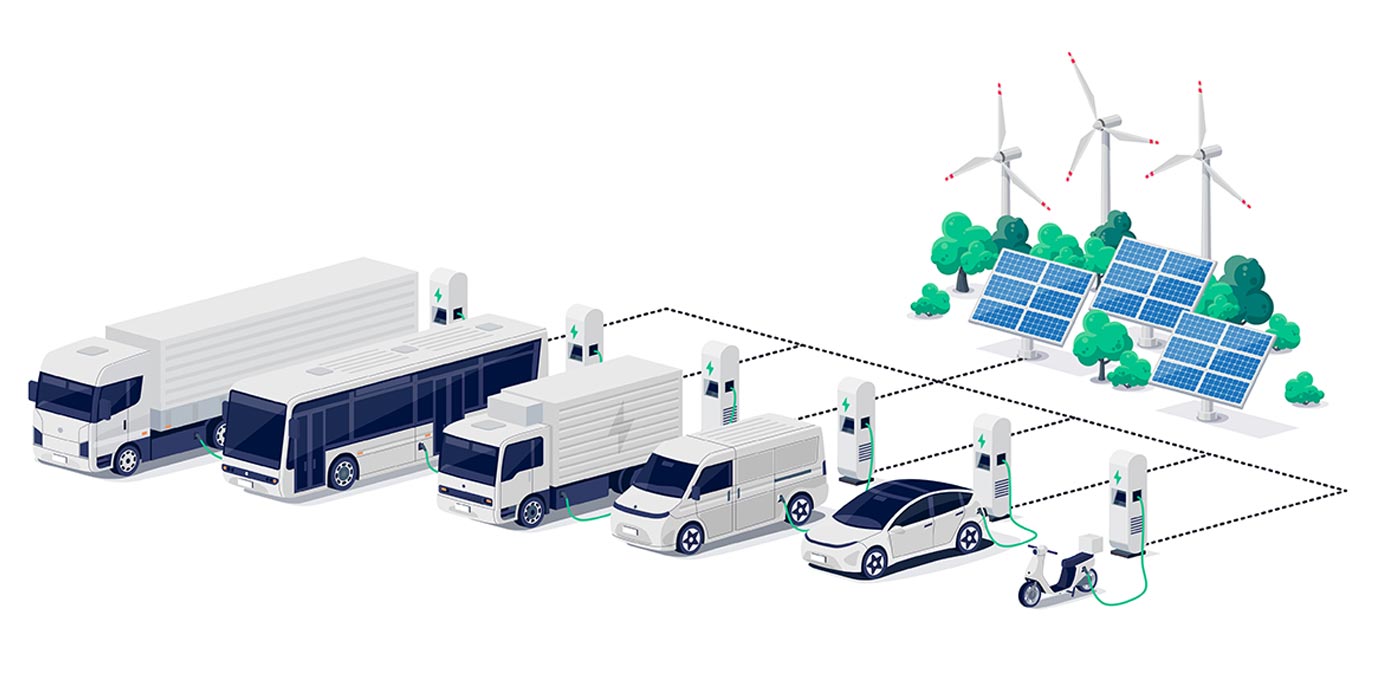
🔋 V2G Energy Flow Model

Applications of V2G
-
Grid Stabilization
V2G-equipped EVs can help balance supply and demand during peak hours, reducing the need for costly peaker plants. -
Backup Power for Homes
In emergency situations, V2G can power household appliances or even entire homes for limited periods. -
Renewable Energy Integration
By storing excess solar or wind energy, V2G allows the grid to rely more heavily on renewable sources. -
Commercial Fleet Optimization
Companies can earn revenue by participating in demand response programs, especially during vehicle idle periods.

Benefits of V2G
-
Energy Cost Savings: Users can charge when prices are low and discharge during high-demand pricing periods.
-
Grid Reliability: Supports load leveling and prevents blackouts.
-
Environmental Impact: Helps reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based peaker plants.
-
Revenue Generation: V2G participants can earn incentives or payments from utilities.
Challenges and Considerations
-
Battery Degradation: Frequent charging/discharging cycles may accelerate battery wear, though research shows minimal impact under controlled conditions.
-
Infrastructure Requirements: V2G requires bidirectional chargers and utility-ready software infrastructure.
-
Standardization: Currently, only a few vehicle models (e.g., Nissan Leaf) support V2G natively, though more automakers are joining the initiative.
-
Regulatory Frameworks: Utilities and governments must establish pricing models and participation guidelines.
Current V2G Pilot Programs
| Region | Program | Partner | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| California, USA | Pacific Gas & Electric V2G Trial | PG&E + EV Fleet Operators | Supports local grid stress reduction |
| UK | Electric Nation V2G Project | Western Power Distribution | Tests residential V2G participation |
| Japan | Tokyo V2G Network | TEPCO + Nissan | Focused on disaster-resilience energy |
The Future of V2G
With growing EV adoption and increasing strain on electrical grids, V2G presents a compelling solution to modern energy challenges. Experts forecast that by 2030, over 20 million EVs worldwide could be V2G-capable, collectively offering more than 200 GWh of distributed energy storage.
Automakers such as Ford, Hyundai, and Volkswagen have already begun integrating bidirectional charging technology into new models. Meanwhile, charger manufacturers like EVDANCE are exploring smart V2G-ready hardware compatible with evolving grid standards.

Conclusion
V2G is more than just a technical innovation—it represents a shift in how we think about cars, energy, and sustainability. By turning electric vehicles into dynamic energy resources, V2G has the potential to stabilize grids, lower costs, and accelerate the transition to renewable power. For consumers and policymakers alike, embracing V2G is a key step toward a more flexible and resilient energy future.
Author: Lay Wen







Share:
Smart Charging in California: Understanding TOU Rates for EV Owners
Incentivizing Daytime EV Charging in the U.S.: A Key Strategy for Grid Stability and EV Adoption